diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index cb84743..ab6d8b0 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -62,70 +62,6 @@ Dropout rate.
Embedding dropout rate.
- `pool`: string, either `cls` token pooling or `mean` pooling
-## CCT
-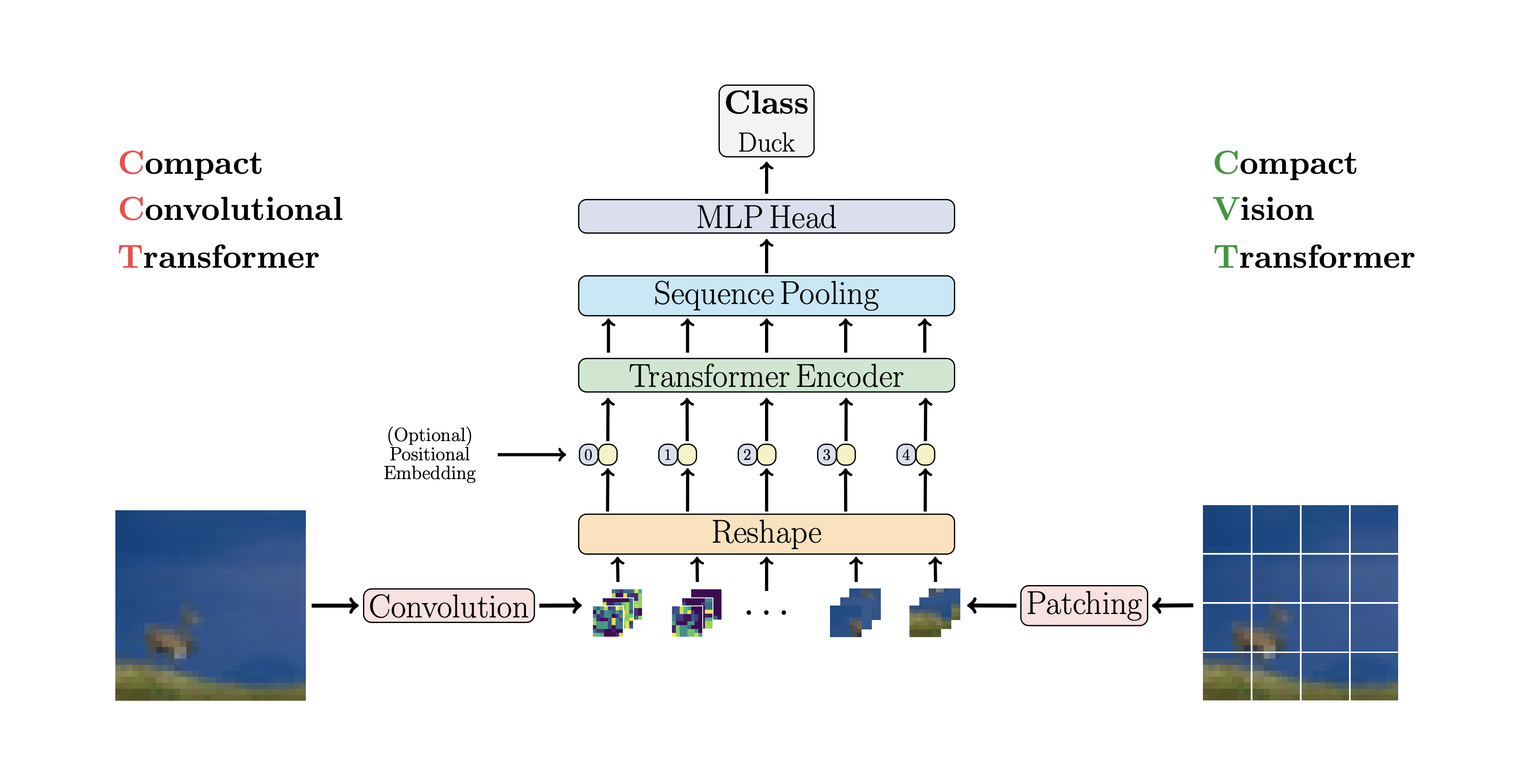 -
-CCT proposes compact transformers
-by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
-allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
-
-You can use this with two methods
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
-
-model = CCT(
- img_size=224,
- embedding_dim=768,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_layers=12,
- num_heads=12,
- mlp_radio=4.,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-
-Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
-which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
-and the embedding dimension.
-
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_2
-
-model = cct_2(
- img_size=224,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-Official
-Repository
-
## Distillation
@@ -267,6 +203,61 @@ img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
preds = v(img) # (1, 1000)
```
+## CCT
+
-
-CCT proposes compact transformers
-by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
-allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
-
-You can use this with two methods
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
-
-model = CCT(
- img_size=224,
- embedding_dim=768,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_layers=12,
- num_heads=12,
- mlp_radio=4.,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-
-Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
-which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
-and the embedding dimension.
-
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_2
-
-model = cct_2(
- img_size=224,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-Official
-Repository
-
## Distillation
@@ -267,6 +203,61 @@ img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
preds = v(img) # (1, 1000)
```
+## CCT
+ +
+CCT proposes compact transformers
+by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
+allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
+
+You can use this with two methods
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
+
+model = CCT(
+ img_size=224,
+ embedding_dim=384,
+ n_conv_layers=2,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_layers=14,
+ num_heads=6,
+ mlp_radio=3.,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+
+Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
+which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
+and the embedding dimension.
+
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_14
+
+model = cct_14(
+ img_size=224,
+ n_conv_layers=1,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+Official
+Repository includes links to pretrained model checkpoints.
+
+
## Cross ViT
+
+CCT proposes compact transformers
+by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
+allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
+
+You can use this with two methods
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
+
+model = CCT(
+ img_size=224,
+ embedding_dim=384,
+ n_conv_layers=2,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_layers=14,
+ num_heads=6,
+ mlp_radio=3.,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+
+Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
+which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
+and the embedding dimension.
+
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_14
+
+model = cct_14(
+ img_size=224,
+ n_conv_layers=1,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+Official
+Repository includes links to pretrained model checkpoints.
+
+
## Cross ViT
 diff --git a/vit_pytorch/cct.py b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
index 1776b12..08219a6 100644
--- a/vit_pytorch/cct.py
+++ b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
@@ -3,7 +3,8 @@ import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Pre-defined CCT Models
-__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_16']
+__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_14', 'cct_16']
+
def cct_2(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=2, num_heads=2, mlp_ratio=1, embedding_dim=128,
@@ -39,6 +40,7 @@ def cct_16(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=16, num_heads=6, mlp_ratio=3, embedding_dim=384,
*args, **kwargs)
+
def _cct(num_layers, num_heads, mlp_ratio, embedding_dim,
kernel_size=3, stride=None, padding=None,
*args, **kwargs):
@@ -81,6 +83,7 @@ class Attention(nn.Module):
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
+
class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Inspired by torch.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer and
@@ -143,6 +146,7 @@ class DropPath(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
+
class Tokenizer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
kernel_size, stride, padding,
diff --git a/vit_pytorch/cct.py b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
index 1776b12..08219a6 100644
--- a/vit_pytorch/cct.py
+++ b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
@@ -3,7 +3,8 @@ import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Pre-defined CCT Models
-__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_16']
+__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_14', 'cct_16']
+
def cct_2(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=2, num_heads=2, mlp_ratio=1, embedding_dim=128,
@@ -39,6 +40,7 @@ def cct_16(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=16, num_heads=6, mlp_ratio=3, embedding_dim=384,
*args, **kwargs)
+
def _cct(num_layers, num_heads, mlp_ratio, embedding_dim,
kernel_size=3, stride=None, padding=None,
*args, **kwargs):
@@ -81,6 +83,7 @@ class Attention(nn.Module):
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
+
class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Inspired by torch.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer and
@@ -143,6 +146,7 @@ class DropPath(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
+
class Tokenizer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
kernel_size, stride, padding,
 -
-CCT proposes compact transformers
-by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
-allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
-
-You can use this with two methods
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
-
-model = CCT(
- img_size=224,
- embedding_dim=768,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_layers=12,
- num_heads=12,
- mlp_radio=4.,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-
-Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
-which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
-and the embedding dimension.
-
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_2
-
-model = cct_2(
- img_size=224,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-Official
-Repository
-
## Distillation
@@ -267,6 +203,61 @@ img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
preds = v(img) # (1, 1000)
```
+## CCT
+
-
-CCT proposes compact transformers
-by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
-allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
-
-You can use this with two methods
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
-
-model = CCT(
- img_size=224,
- embedding_dim=768,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_layers=12,
- num_heads=12,
- mlp_radio=4.,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-
-Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
-which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
-and the embedding dimension.
-
-```python
-import torch
-from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_2
-
-model = cct_2(
- img_size=224,
- n_input_channels=3,
- n_conv_layers=1,
- kernel_size=7,
- stride=2,
- padding=3,
- pooling_kernel_size=3,
- pooling_stride=2,
- pooling_padding=1,
- num_classes=1000,
- dropout_rate=0.1,
- attention_dropout=0.1,
- stochastic_depth_rate=0.1,
- positional_embedding='sine', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
- sequence_length=None,
- )
-```
-Official
-Repository
-
## Distillation
@@ -267,6 +203,61 @@ img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
preds = v(img) # (1, 1000)
```
+## CCT
+ +
+CCT proposes compact transformers
+by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
+allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
+
+You can use this with two methods
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
+
+model = CCT(
+ img_size=224,
+ embedding_dim=384,
+ n_conv_layers=2,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_layers=14,
+ num_heads=6,
+ mlp_radio=3.,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+
+Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
+which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
+and the embedding dimension.
+
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_14
+
+model = cct_14(
+ img_size=224,
+ n_conv_layers=1,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+Official
+Repository includes links to pretrained model checkpoints.
+
+
## Cross ViT
+
+CCT proposes compact transformers
+by using convolutions instead of patching and performing sequence pooling. This
+allows for CCT to have high accuracy and a low number of parameters.
+
+You can use this with two methods
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import CCT
+
+model = CCT(
+ img_size=224,
+ embedding_dim=384,
+ n_conv_layers=2,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_layers=14,
+ num_heads=6,
+ mlp_radio=3.,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+
+Alternatively you can use one of several pre-defined models `[2,4,6,7,8,14,16]`
+which pre-define the number of layers, number of attention heads, the mlp ratio,
+and the embedding dimension.
+
+```python
+import torch
+from vit_pytorch.cct import cct_14
+
+model = cct_14(
+ img_size=224,
+ n_conv_layers=1,
+ kernel_size=7,
+ stride=2,
+ padding=3,
+ pooling_kernel_size=3,
+ pooling_stride=2,
+ pooling_padding=1,
+ num_classes=1000,
+ positional_embedding='learnable', # ['sine', 'learnable', 'none']
+ )
+```
+Official
+Repository includes links to pretrained model checkpoints.
+
+
## Cross ViT
 diff --git a/vit_pytorch/cct.py b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
index 1776b12..08219a6 100644
--- a/vit_pytorch/cct.py
+++ b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
@@ -3,7 +3,8 @@ import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Pre-defined CCT Models
-__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_16']
+__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_14', 'cct_16']
+
def cct_2(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=2, num_heads=2, mlp_ratio=1, embedding_dim=128,
@@ -39,6 +40,7 @@ def cct_16(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=16, num_heads=6, mlp_ratio=3, embedding_dim=384,
*args, **kwargs)
+
def _cct(num_layers, num_heads, mlp_ratio, embedding_dim,
kernel_size=3, stride=None, padding=None,
*args, **kwargs):
@@ -81,6 +83,7 @@ class Attention(nn.Module):
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
+
class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Inspired by torch.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer and
@@ -143,6 +146,7 @@ class DropPath(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
+
class Tokenizer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
kernel_size, stride, padding,
diff --git a/vit_pytorch/cct.py b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
index 1776b12..08219a6 100644
--- a/vit_pytorch/cct.py
+++ b/vit_pytorch/cct.py
@@ -3,7 +3,8 @@ import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Pre-defined CCT Models
-__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_16']
+__all__ = ['cct_2', 'cct_4', 'cct_6', 'cct_7', 'cct_8', 'cct_14', 'cct_16']
+
def cct_2(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=2, num_heads=2, mlp_ratio=1, embedding_dim=128,
@@ -39,6 +40,7 @@ def cct_16(*args, **kwargs):
return _cct(num_layers=16, num_heads=6, mlp_ratio=3, embedding_dim=384,
*args, **kwargs)
+
def _cct(num_layers, num_heads, mlp_ratio, embedding_dim,
kernel_size=3, stride=None, padding=None,
*args, **kwargs):
@@ -81,6 +83,7 @@ class Attention(nn.Module):
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
+
class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Inspired by torch.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer and
@@ -143,6 +146,7 @@ class DropPath(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
+
class Tokenizer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
kernel_size, stride, padding,